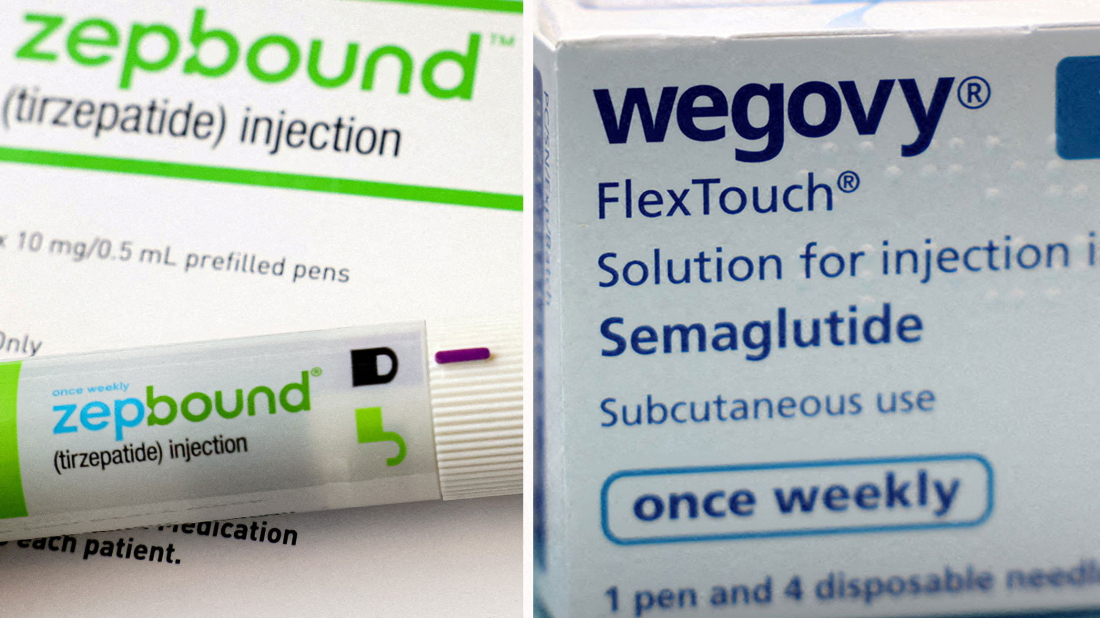
The World Health Organization is set to recommend weight-loss drugs like Wegovy and Zepbound for treating obesity in adults, marking its first official backing of such medications and signaling a major shift in global health policy.
-The World Health Organization plans to officially back the use of weight-loss drugs to treat obesity in adults for the first time, a memo reviewed by Reuters on Thursday shows, marking a shift in its approach to treating the global health problem.
The UN agency also called for strategies to improve access to the treatment in low- and middle-income countries.
More than a billion people now have obesity worldwide, according to the WHO, and around 70% of them live in low and middle-income countries, the World Bank estimates.
The wildly popular obesity drugs - Wegovy developed by Novo Nordisk and Zepbound by Eli Lilly - are known as GLP-1 receptor agonists, which mimic the activity of a hormone that slows digestion and helps people feel full for longer. In clinical trials, people lost 15% to 20% of their body weight, depending on the drug.
The drugs have been launched in the United States and other high-income countries like Germany and Britain.
But they can cost over $1,000 a month, and studies suggest people may have to take the drugs for the rest of their lives to keep the weight off.
The WHO, Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk were not immediately available for comment.
The WHO's conditional recommendation will be officially released in August, as part of new guidelines on treating obesity. It is also working on separate guidelines for children and adolescents.
Separately, WHO experts will also meet next week to decide whether to include the GLP-1 drugs in the agency's essential medicines list - both to treat obesity and type 2 diabetes.
The WHO's essential medicines list is a catalogue of the drugs that should be available in all functioning health systems, and it can help make drugs more widely available in poorer countries, as experts say happened in 2002 when HIV drugs were included.
In 2023, the experts decided against adding obesity drugs to the list, with WHO saying more evidence was needed on their long-term clinical benefit.
However, in the new memo recommending their use as a treatment, the agency says it supports including them on the list this time round.
Still, the WHO also raises concerns over the cost of the drugs and calls for longer-term studies on cost-effectiveness "across all settings, including LMICs" (low- and middle-income countries).
"The same mechanisms that are used in large-scale medicine access programmes may need to be adopted," to improve access, the WHO adds, such as tiered pricing or pooled procurement.
But it also notes that the active ingredient in one of the newer drugs, semaglutide - used in Novo's Wegovy - comes off patent in some markets next year.
Several companies are planning to launch cheaper generic versions of the drugs then. Liraglutide, the active ingredient in the older generation of drugs, is already available as a lower-cost generic drug, with products approved in the U.S. and Europe, the memo adds.


















What is your opinion on this topic?
Leave the first comment