Oil prices hit four year high: Latest news on the Middle East conflict on 9 March
Global oil prices reached a four year high on Monday (9 March), surpassing $...
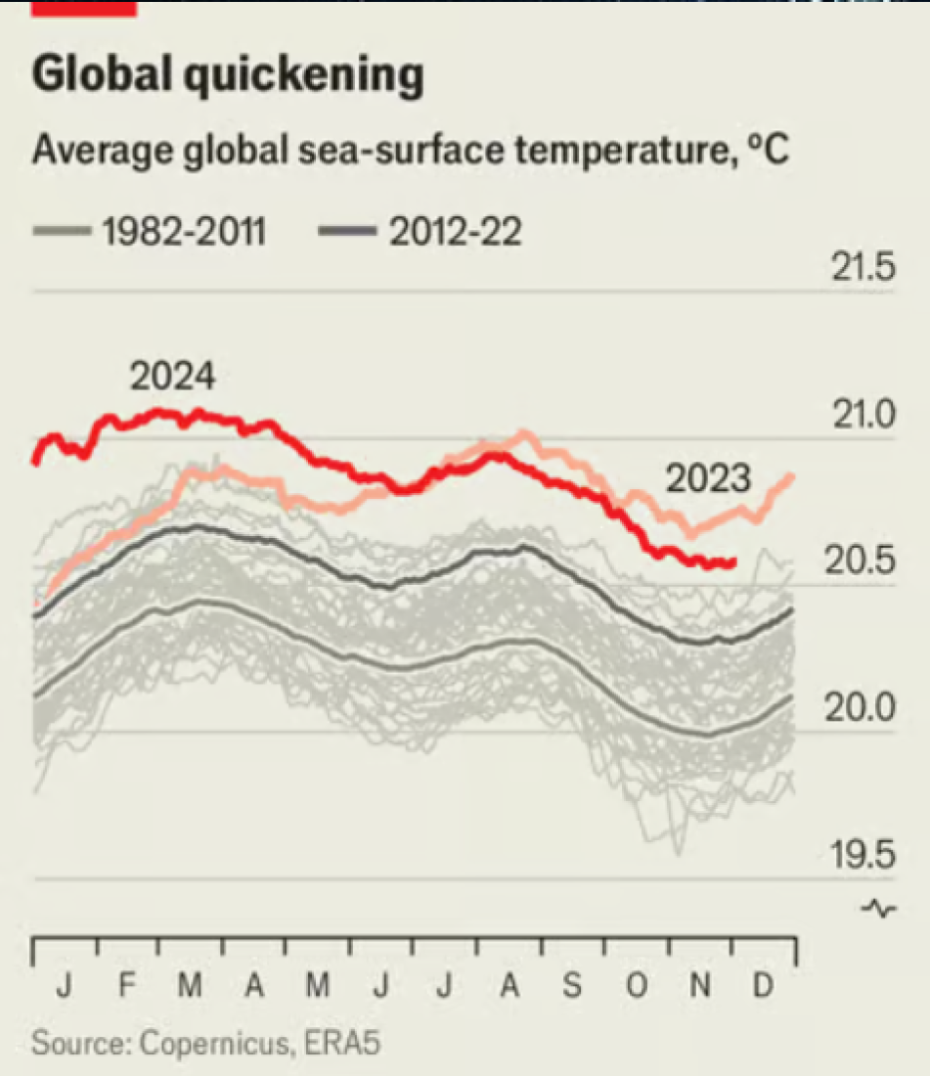
2023 defied climate expectations. It wasn’t just hotter than predicted — it was strangely hot. Now, scientists are piecing together what caused this anomaly, raising fresh concerns about Earth’s climate systems.
Gavin Schmidt, NASA’s top climate modeller at the Goddard Institute for Space Science, admitted to feeling “humbled” by 2023’s extraordinary temperatures. Writing in Nature earlier this year, Schmidt noted that the year was warmer than models anticipated. The deviation, unexplained at first, sparked worries that climate change is entering uncharted territory.
At December’s American Geophysical Union (AGU) meeting, the world's largest Earth science conference, experts revisited the mystery. Like detectives solving a case, scientists meticulously ruled out some “suspects” while identifying others.
Key Suspects Behind the Heat Surge
El Niño
The natural El Niño event, which warms the tropical Pacific, began in 2023, contributing to global temperatures. Yet the warming exceeded even El Niño’s usual influence, raising eyebrows.
Cleaner Air from Shipping
New rules to reduce sulphur in ship fuel have lowered pollution levels. However, cleaner air allows more sunlight to reach the ocean surface, which adds to global warming.
Volcano and Solar Activity
The Hunga Tonga eruption in 2022 injected water vapour into the atmosphere but also sulphates, which slightly cooled the Earth. Meanwhile, the Sun reached its peak activity cycle, contributing minimal extra heat.
Cloud Cover Changes
Research by Germany’s Alfred Wegener Institute found Earth reflected less sunlight in 2023 — its dimmest year yet. Reduced cloud cover, particularly over northern mid-latitudes, amplified warming. Cleaner air may have played a role, alongside long-term climate shifts that are altering cloud patterns.
The Bigger Picture
Global warming is accelerating. Some scientists argue that the drop in sulphur emissions is now speeding up heating, while changing cloud dynamics add to the uncertainty.
What’s Next
GISS modellers are now combining the latest data on sulphur emissions, cloud dynamics, and sunlight reflectivity into updated climate simulations. Schmidt expects these runs to clarify the contributions of various factors and potentially reshape projections for Earth’s future.
The findings are clear: warming is unlikely to slow any time soon.
Mojtaba Khamenei, son of the late Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, is a hardline cleric with strong backing from the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps. His rise signals continuity in Tehran's anti-Western policies.
Trump says the United States "don’t need people that join wars after we’ve already won," targeting his criticism at UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer. Israel continues to fire missles at strategic sites in Iran and Gulf regions report more strikes from Iran.
Global oil prices surpassed $119 a barrel on Monday (9 March, 2026), an almost four year high, as the Middle East conflict rumbled on.
Iran named Mojtaba Khamenei to succeed his father Ali Khamenei as supreme leader on Monday (9 March), signaling that hardliners remain firmly in charge, as the week-old U.S.-Israeli war with Iran pushed oil above $100 a barrel.
Entry and exit across the state border between Azerbaijan and Iran for all types of cargo vehicles, including those in transit, will resume on 9 March, according to a statement by the Cabinet of Ministers of Azerbaijan.
The death toll from heavy rains and flooding in Brazil’s Minas Gerais state has risen to 46, authorities said, with 21 people still reported missing. The storms triggered landslides and widespread flooding, displacing thousands across Juiz de Fora and Uba.
The administration of U.S. President Donald Trump on Thursday (12 February) announced the repeal of a scientific finding that greenhouse gas emissions endanger human health, and eliminated federal tailpipe emissions standards for cars and trucks.
Tropical Cyclone Gezani has killed at least 31 people and left four others missing after tearing through eastern Madagascar, the government said on Wednesday, with the island nation’s second-largest city bearing the brunt of the destruction.
Rivers and reservoirs across Spain and Portugal were on the verge of overflowing on Wednesday as a new weather front pounded the Iberian peninsula, compounding damage from last week's Storm Kristin.
Morocco has evacuated more than 100,000 people from four provinces after heavy rainfall triggered flash floods across several northern regions, the Interior Ministry said on Wednesday.
You can download the AnewZ application from Play Store and the App Store.

What is your opinion on this topic?
Leave the first comment