French scientists have set a new record by maintaining high-temperature plasma for 22 minutes, bringing the world closer to the promise of nuclear fusion as a clean, sustainable energy source.
On Tuesday, French scientists announced a significant achievement in the pursuit of nuclear fusion, reaching a "crucial milestone" that could pave the way toward cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. The breakthrough was marked by the successful maintenance of high-temperature plasma for a record 22 minutes—an important step in overcoming one of the most challenging aspects of nuclear fusion.
Nuclear fusion, the process that powers stars, has long been hailed as a potential solution to the world’s energy needs. Unlike nuclear fission, which splits atomic nuclei to release energy (as in conventional nuclear power plants), fusion combines two atomic nuclei to form a heavier one, releasing vast amounts of energy. If harnessed effectively, fusion could provide nearly limitless, safe, and environmentally friendly energy, making it a coveted technological goal for scientists worldwide.
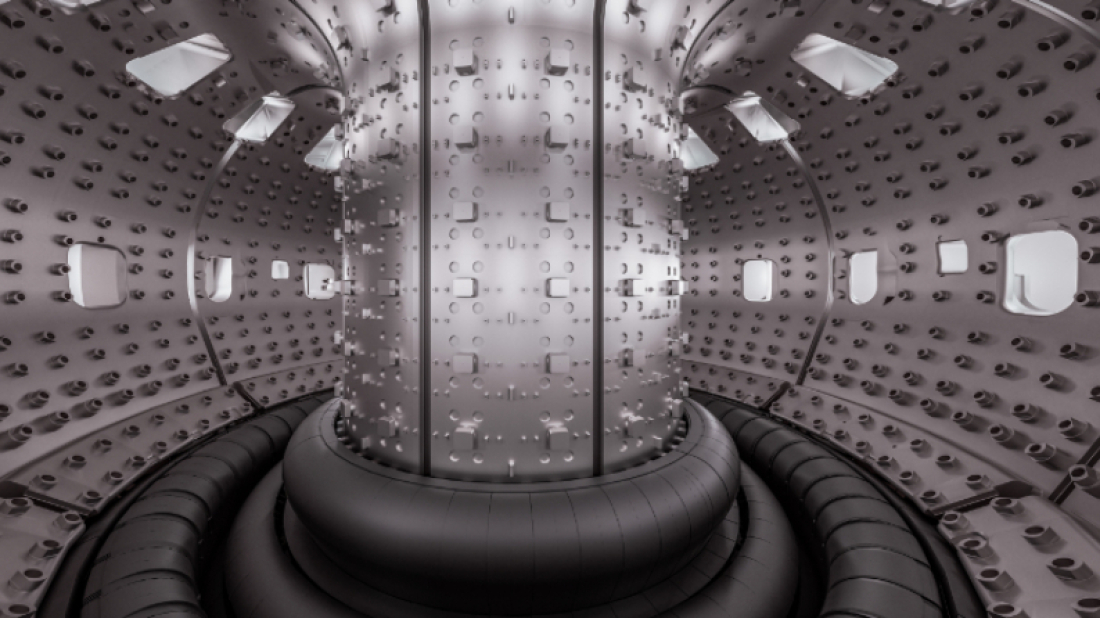
The process of fusion, however, is far from simple. Achieving the extreme conditions required—temperatures exceeding 100 million degrees Celsius—is one of the most significant obstacles to its realization. At these temperatures, the plasma (a hot, electrically charged gas) becomes highly unstable, posing challenges to both energy efficiency and the longevity of the reactors used in fusion research.
The breakthrough came at the WEST tokamak machine in southern France, which was able to sustain plasma for an impressive 1,337 seconds on February 12. This achievement surpassed the previous record set by China in January by 25 percent, marking a considerable step forward. According to France’s Atomic Energy Commission (CEA), this success demonstrates not only the ability to generate plasma but also to maintain it over extended periods, signaling greater control over the fusion process.
Anne-Isabelle Etienvre, head of fundamental research at CEA, emphasized the significance of this accomplishment. "This milestone proves that we can not only produce plasma, but also maintain it with a high degree of stability," she stated. However, she acknowledged that much work remains to be done before thermonuclear fusion can achieve the ultimate goal: generating more energy than it consumes.
Looking ahead, the team at WEST has ambitious plans to extend the duration of plasma maintenance even further—aiming for durations of several hours in the coming months. Additionally, they will work toward reaching even higher temperatures in order to simulate the conditions expected in future fusion reactors. These advancements are crucial steps in preparing for the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), a collaborative global project being built in France.
The ITER project, which began in 1985, brings together partners from China, the European Union, India, Japan, South Korea, Russia, and the United States. Initially slated to go online in the coming years, ITER's timeline has been delayed due to a series of setbacks, and it is now expected to begin operations no earlier than 2033. The successful progress made at the WEST tokamak, however, offers hope that fusion energy is slowly becoming a reality, inching closer to the day when it could become a viable, clean, and nearly inexhaustible source of power.
While challenges remain, the recent progress in plasma containment and stability marks a pivotal step in the decades-long pursuit of nuclear fusion. As research continues, scientists remain hopeful that the long-awaited fusion revolution could transform the global energy landscape, offering a path toward a more sustainable and energy-secure future.






















What is your opinion on this topic?
Leave the first comment