Kyrgyzstan sees world’s biggest jump in women MPs, new report finds
Kyrgyzstan recorded the largest increase in women’s representation in parliament worldwide in 2025, accordin...
You’ve probably heard of quantum computing, the mysterious new tech that promises to change everything from drug development to cybersecurity. But what is it really, and why is it such a big deal? Let’s break it down in plain English.
A new kind of computer
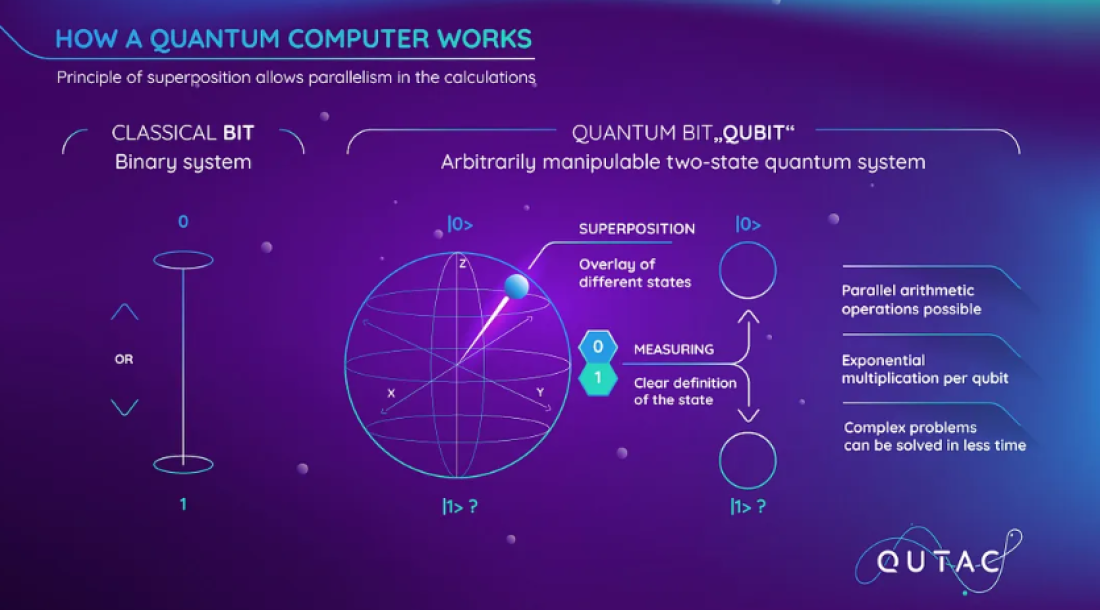
Today’s computers, laptops, smartphones, even supercomputers, all speak the same basic language. They process information using bits, which can either be a 0 or a 1. That’s how everything from emails to Netflix streams are built.
Quantum computers, on the other hand, use qubits (short for "quantum bits"). These are totally different. Thanks to the strange rules of quantum physics, qubits can be both 0 and 1 at the same time. Think of it like a coin spinning in the air, showing heads and tails at once.
This idea is called superposition, and it gives quantum computers their massive power.
“Quantum computing is not just faster computing. It’s a fundamentally new way of processing information.”
— Scott Aaronson, Professor of Computer Science, University of Texas at Austin
What makes them special?
Two big ideas make quantum computers powerful:
Superposition: Qubits can hold more information than regular bits, because they exist in multiple states at once.
Entanglement: Qubits can be connected in such a way that changing one affects the other, even if they’re far apart.
Because of this, a quantum computer can process many possibilities at the same time, finding solutions to complex problems much faster than today’s machines.
“Think of a quantum computer as a parallel universe calculator. It doesn’t go faster, it goes wider.”
— Michelle Simmons, Director, Centre for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology
So, why does it matter?
Quantum computing could help solve problems that are just too difficult, or would take too long, for regular computers. Some real-world examples include:
Faster drug discovery
Testing how new molecules interact could become quicker and more precise.
Better manufacturing
Simulating prototypes or predicting material behaviour with greater accuracy.
Traffic and route optimisation
Helping cities and companies plan faster, more efficient routes.
Advanced financial modelling
Analysing market risks and patterns far beyond today's capabilities.
“Quantum computers will change the way we think about problems we thought were impossible to solve.”
— Dario Gil, Director of IBM Research
But there’s a catch…
Quantum computing isn’t just exciting, it’s also risky, especially when it comes to security.
Most of today’s encryption (which keeps your online data safe) relies on problems that are hard for classical computers to solve. But quantum computers might crack those codes quickly, making current security systems vulnerable.
“Quantum computing poses both an existential threat and a revolutionary opportunity for cybersecurity.”
— Michele Mosca, Co-founder, Institute for Quantum Computing
That’s why researchers are now working on post-quantum cryptography — new kinds of security to stay ahead of future threats.
“Post-quantum cryptography must become a priority today, not tomorrow.”
— Anne Neuberger, U.S. Deputy National Security Advisor for Cyber and Emerging Technology
Are we there yet?
Not quite. As of now, no quantum computer is powerful enough to consistently outperform traditional machines in practical tasks. Experts call this milestone quantum advantage, and are're still working towards it.
“We haven’t reached quantum advantage yet, but the race is on — and progress is accelerating fast.”
— John Preskill, Theoretical Physicist, Caltech
But governments, tech giants, and startups are pouring billions into research. According to Tractica, global investment in quantum technology could reach $9.1 billion by 2030.
What’s inside a quantum computer?
Just like regular computers, quantum computers have hardware and software — but with a quantum twist.
Quantum hardware: Uses physical qubits made from atoms, ions, or even light.
Quantum software: Includes special algorithms that take advantage of quantum effects like superposition and entanglement.
Because qubits are fragile and easily disturbed by their environment (a problem called decoherence), quantum machines are kept in super-cooled labs, often close to absolute zero.
“It’s like the early days of flight, we're still learning how to leave the ground, but the impact will be enormous.”
— Shohini Ghose, Quantum physicist and author
Different types of quantum machines
There’s no one way to build a quantum computer. Here are some of the most promising methods:
Trapped ion processors – use charged atoms controlled by lasers
Superconducting qubits – use electric circuits cooled to freezing temperatures
Photonic processors – use light particles to do calculations
Quantum annealers – specialise in optimisation problems
Neutral atom & Rydberg atom processors – use atoms manipulated by light or excited electron states
Who’s using quantum computing?
Quantum computing is still in early stages, but several industries are already exploring its potential:
Healthcare – for simulating molecules in drug research
Manufacturing – to improve supply chains and reduce waste
Finance – to optimise portfolios and manage risk
Climate science – to model complex systems like weather and ecosystems
AI and Machine Learning – to speed up training and discover new algorithms
“In the future, countries that master quantum computing will set the rules for cybersecurity, AI, and global finance.”
— Arvind Krishna, Chairman and CEO, IBM
Want to try it yourself?
You don’t need to be a physicist to get started. Several companies now offer cloud-based quantum computing, where you can write and test quantum programs, no lab required.
Services like Amazon Braket, IBM Quantum, and Google Quantum AI let users and researchers experiment with real quantum hardware or simulators from anywhere in the world.
Final thoughts
Quantum computing isn’t magic, but it is a game-changer.
From scientific breakthroughs to new industries, this technology has the potential to transform our world. But like any powerful tool, it must be developed responsibly, with careful attention to ethics, security, and accessibility.
We’re still in the early days, but the quantum future is closer than you think.
Mojtaba Khamenei, son of the late Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, is a hardline cleric with strong backing from the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps. His rise signals continuity in Tehran's anti-Western policies.
Trump says the United States "don’t need people that join wars after we’ve already won," targeting his criticism at UK Prime Minister Keir Starmer. Israel continues to fire missles at strategic sites in Iran and Gulf regions report more strikes from Iran.
Global oil prices surpassed $119 a barrel on Monday (9 March, 2026), an almost four year high, as the Middle East conflict rumbled on.
Iran named Mojtaba Khamenei to succeed his father Ali Khamenei as supreme leader on Monday (9 March), signaling that hardliners remain firmly in charge, as the week-old U.S.-Israeli war with Iran pushed oil above $100 a barrel.
Entry and exit across the state border between Azerbaijan and Iran for all types of cargo vehicles, including those in transit, will resume on 9 March, according to a statement by the Cabinet of Ministers of Azerbaijan.
Chinese electric vehicle giant BYD is pushing to make charging an electric car almost as quick and convenient as filling up a traditional petrol vehicle - a move that could help remove one of the biggest barriers to wider electric vehicle adoption.
South Korea will soon cease to be one of the few countries where Google Maps does not function fully, after its security-conscious government reversed a two-decade-old policy and approved the export of high-precision map data to overseas servers.
New research suggests 40,000-year-old carved objects from south-western Germany bear repeated marks arranged in organised sign sequences similar to early proto-cuneiform, although they are not regarded as a form of writing.
The chief executive of Google DeepMind, Demis Hassabis, has called for more urgent research into the risks posed by artificial intelligence, warning that stronger safeguards are needed as systems become more advanced.
NASA successfully completed a critical fueling rehearsal on Thursday (19 February) for its giant moon rocket, Artemis II, after earlier hydrogen leaks disrupted preparations for the next crewed lunar mission. The launch is scheduled for 6 March, according to the latest information from NASA.
You can download the AnewZ application from Play Store and the App Store.

What is your opinion on this topic?
Leave the first comment