As South Korea hosts INC-5 talks on plastic waste, critics say its 73% recycling claim hides flaws, with actual rates near 27%. Rising plastic use and financial challenges reveal limits of recycling-focused strategies.
Despite international recognition for its recycling efforts, South Korea’s challenges with plastic waste are coming into sharper focus as it prepares to host the INC-5 talks in Busan next week. The discussions will center on a potential global agreement to address plastic pollution, with contentious debates expected over whether the treaty should include limits on plastic production.
Countries like Saudi Arabia and China, major plastic and petrochemical producers, oppose such restrictions, advocating instead for improved waste management practices.
South Korea reports recycling 73% of its plastic waste, compared to the United States’ 5-6%, earning it praise as one of the top recycling nations. The MIT Technology Review even ranked South Korea as the only Asian country in the top 10 of its 2022 Green Future Index.
However, critics argue these statistics are misleading. Seo Hee-won of the Climate Change Center says the 73% figure reflects plastic that reaches screening facilities, without clarity on how much is actually recycled versus incinerated or sent to landfills. Greenpeace estimates the true recycling rate is closer to 27%.
The country’s plastic waste problem has grown significantly, with annual generation rising from 9.6 million tonnes in 2019 to 12.6 million tonnes in 2022—a 31% increase driven by the pandemic-related surge in online shopping and packaging.
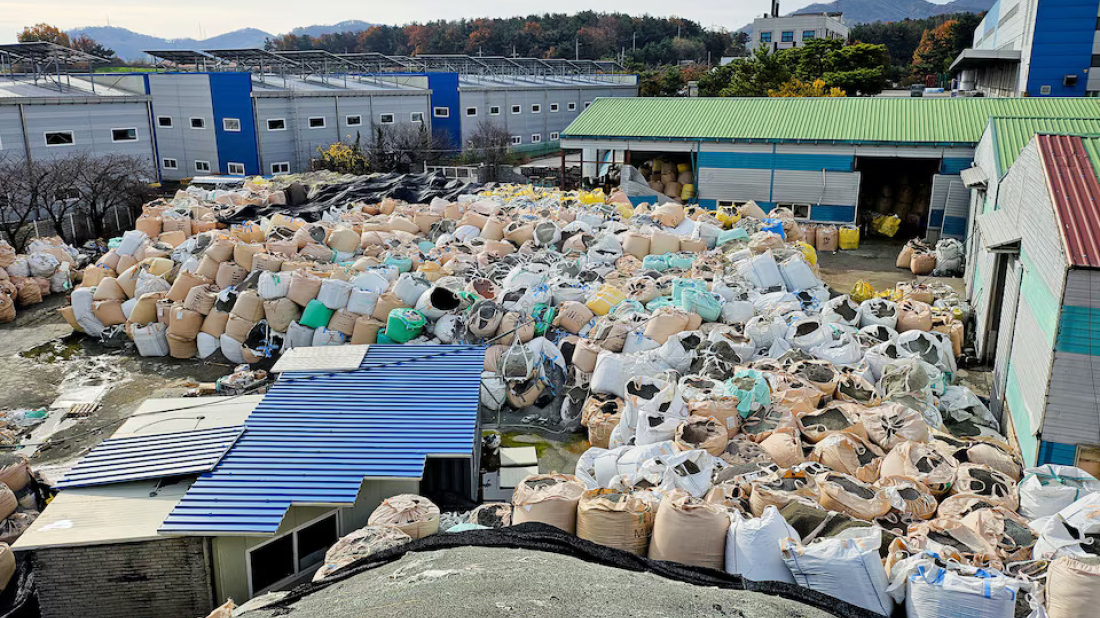
Financial challenges have further hindered recycling. At a closed recycling facility in Asan, approximately 19,000 tonnes of untreated plastic waste remain piled up, emitting foul odors. Local officials attribute the issue to the facility owner’s financial difficulties, estimating cleanup costs between $1.43 million and $2.14 million—a low priority due to the lack of funding.
South Korea’s situation highlights the complexities and limitations of recycling-focused approaches, raising questions about the need for more aggressive measures to curb plastic production globally.






















What is your opinion on this topic?
Leave the first comment