live Trump cites Churchill in taunt at Starmer over Iran: All the latest news on the Iran strikes
U.S. President Donald Trump said the U.S. military has enough stockpiled weapons to fight wars "forever"; in a...
The question of whether the United States will join Israel militarily through direct troop deployments has become one of the most pressing foreign policy issues of 2025.
Based on extensive analysis of official statements, congressional records, and military cooperation data, this comprehensive examination reveals a complex landscape where the U.S. has already deployed limited military personnel to Israel while facing significant constitutional, political, and public opinion constraints on expanded involvement.
Current Military Presence: American Troops Already in Israel
THAAD Deployment Marks Historic Threshold
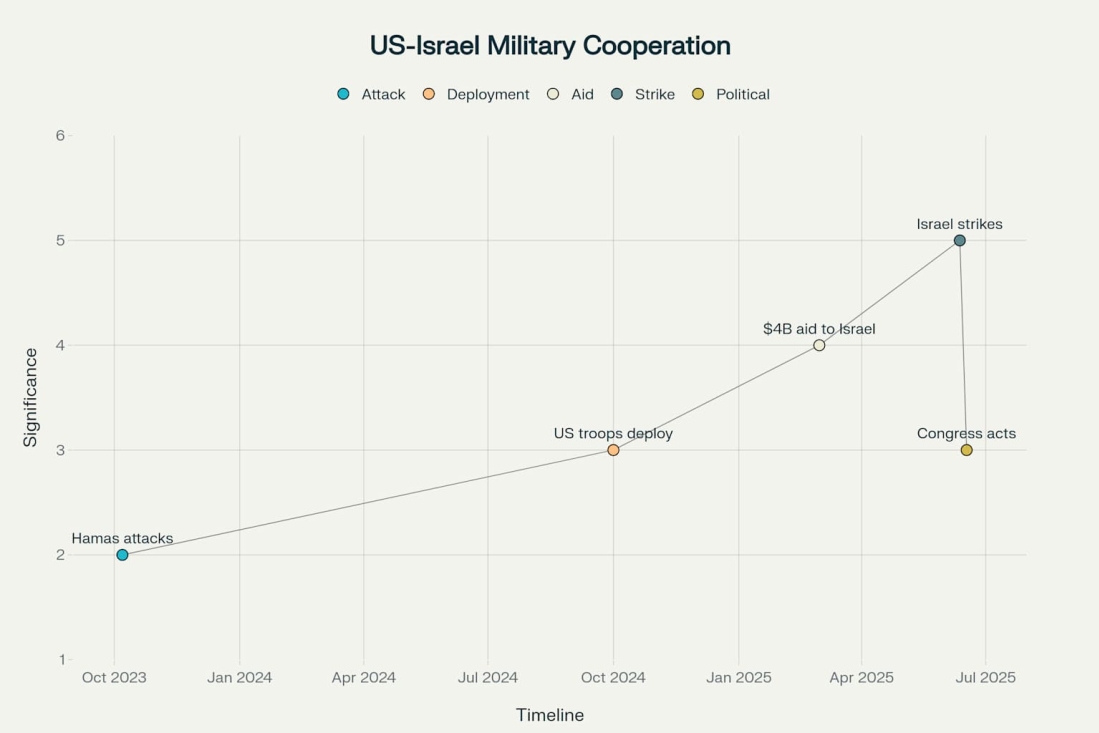
The United States has already crossed a significant milestone by deploying approximately 100 military personnel to Israel as of October 2024. These troops operate the Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) anti-missile system, marking the first time American forces have been stationed on Israeli soil during the current conflict. Pentagon Press Secretary Patrick Ryder confirmed this deployment demonstrates "the United States' ironclad commitment to the defense of Israel".
The THAAD system deployment followed Iran's unprecedented ballistic missile attacks against Israel in April and October 2024. This mobile defense system can intercept both short- and medium-range ballistic missiles, significantly enhancing Israel's defensive capabilities. The deployment was classified as defensive in nature and authorized under executive authority without requiring congressional approval.
Expanding Naval and Air Support
Beyond ground deployments, U.S. military involvement has expanded significantly since October 7, 2023. American forces participated directly in defensive operations, with U.S. fighter jets joining allies from the U.K., France, and Jordan in April 2024 to intercept Iranian drones and missiles targeting Israel. The U.S. Navy deployed the USS Abraham Lincoln Carrier Strike Group equipped with F-35C Lightning II combat jets and the ballistic missile submarine USS Georgia to the region.
Intelligence operations represent another significant component of U.S. involvement. According to available data, U.S. aircraft have been responsible for 33% of reconnaissance flights providing Israel with intelligence on ground movements in Gaza. Recent escalations in June 2025 have seen additional deployments of U.S. Air Force fighters to bases in the Middle East.
Military Aid: Unprecedented Financial Support
Dramatic Escalation Since October 2023
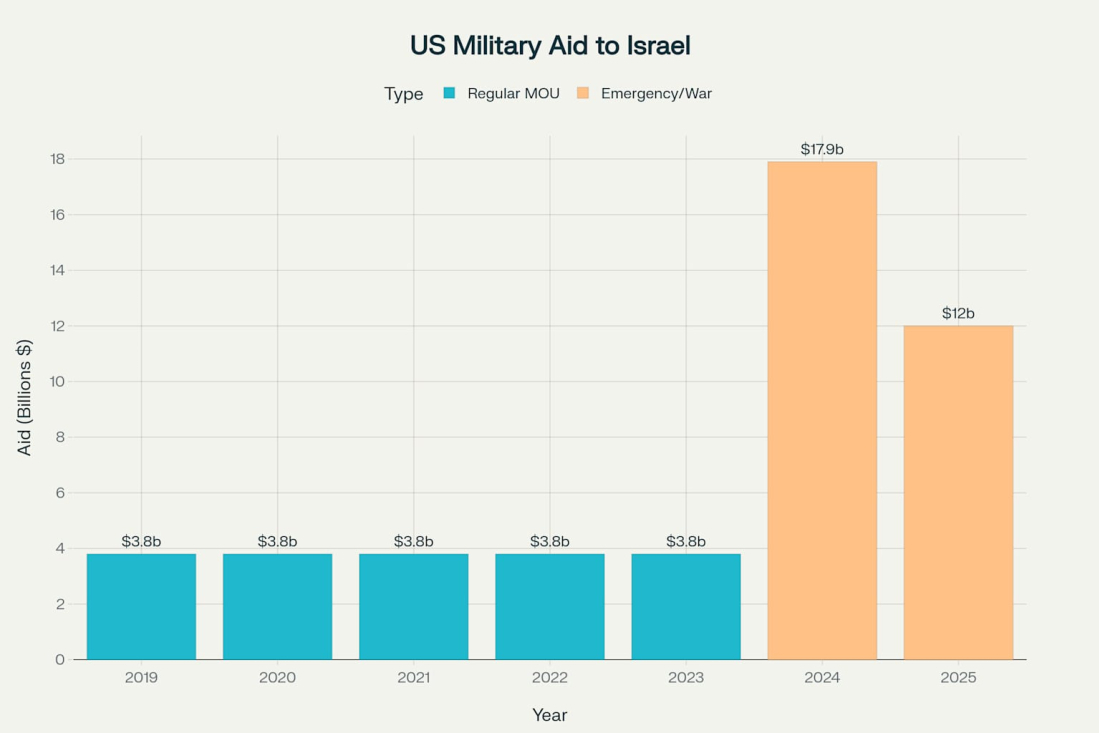
U.S. military aid to Israel has reached historic levels since the October 7, 2023 attacks. The Trump administration has approved approximately $12 billion in major Foreign Military Sales to Israel since taking office in January 2025. In March 2025, Secretary of State Marco Rubio used emergency authorities to expedite approximately $4 billion in military assistance.
Total U.S. spending on Israel's military operations and related regional operations has reached at least $22.76 billion since October 2023. This figure substantially exceeds any previous year since the U.S. began granting military aid to Israel in 1959. The spending represents a dramatic increase from the standard $3.8 billion provided annually under the current 10-year Memorandum of Understanding.
Long-Term Aid Framework
Under the current agreement signed in 2016, the U.S. provides Israel with $3.8 billion annually through 2028. This $38 billion agreement represents the largest military aid package in U.S. history. Since 1946, the United States has provided over $310 billion in military and economic aid to Israel.
Congressional Oversight and Legal Constraints
War Powers Resolution Framework
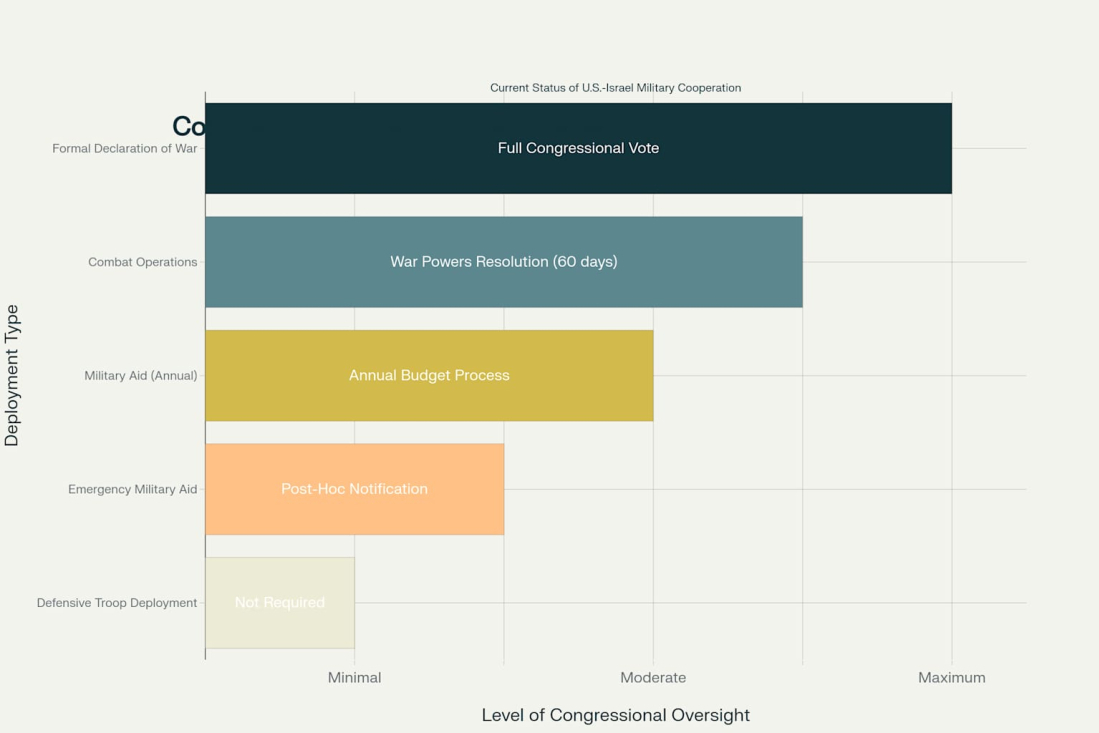
The legal framework governing potential U.S. military involvement centers on the 1973 War Powers Resolution. This legislation requires presidential notification of Congress within 48 hours of committing armed forces to military action and prohibits sustained military engagement beyond 60 days without congressional authorization. The Constitution grants Congress the sole power to declare war.
Current U.S. deployments to Israel fall within a legal gray area. The THAAD system deployment is characterized as defensive and within presidential authority. However, the distinction between defensive and offensive operations becomes increasingly difficult to maintain.
Bipartisan Congressional Response
A significant bipartisan effort emerged in June 2025 to reassert congressional war powers regarding potential military action. Representatives Thomas Massie (R-KY) and Ro Khanna (D-CA) introduced a resolution requiring congressional approval for any U.S. military action against Iran. Senator Tim Kaine (D-VA) introduced similar legislation emphasizing that "the American people are not inclined to send servicemen and women into another endless war in the Middle East".
"This is not our war," Massie stated. "Even if it were, Congress must decide such matters according to our Constitution". Progressive lawmakers have questioned the constitutional authority for current military involvement, arguing that deployment exceeds presidential authority and requires congressional authorization.
Political Dynamics and Public Opinion
Shifting American Attitudes
American public opinion regarding military support for Israel has become increasingly polarized. Recent polling shows Americans give Israel a rating of 50 on a 0-100 scale, the lowest since 1978. More than half of U.S. adults (53%) now express an unfavorable opinion of Israel.
The partisan divide is stark regarding military support. Republicans overwhelmingly support continued military aid (76% favor supporting Israel until hostages are returned), while Democratic support has declined significantly (only 43% support). Polling demonstrates American reluctance to deploy troops to the Middle East, with 52% opposing sending more troops while only 17% support such deployments.
Opposition to Military Engagement
Additionally, 62% of Americans oppose the idea of the U.S. taking control of Gaza, a proposal suggested by President Trump. Public awareness of current military deployments remains limited, with fewer than 30% of respondents aware of U.S. troop presence in Syria. This suggests potential for increased opposition as awareness grows.
Trump Administration Policy Evolution
Balancing Support with Restraint
The Trump administration has demonstrated strong rhetorical support for Israel while showing caution about direct military involvement. President Trump acknowledged having advance knowledge of Israeli strikes against Iran in June 2025, stating "We knew everything" about the operations. Trump's approach reflects tension between supporting allies and fulfilling campaign promises to avoid new foreign wars.
The administration has increased military aid and authorized additional weapons transfers while deploying defensive systems. However, Trump has also called for Iran's "unconditional surrender" and warned that U.S. patience is "wearing thin". According to analysis, "For Trump, the priority remains the safety of American civilian and military personnel deployed in the Middle East".
Expert Analysis and Strategic Assessment
Defense Policy Perspectives
Military and foreign policy experts remain divided on the likelihood of expanded U.S. military involvement. Daniel Byman of the Center for Strategic and International Studies warns that the U.S. "could easily get sucked into this conflict". He suggests that if Iran's nuclear program continues advancing, the administration "might feel that attacking Iran is better than allowing Iran to rebuild its nuclear program".
Other experts point to emerging constraints on U.S.-Israel cooperation. Dan Shapiro, former U.S. ambassador to Israel, observed that "Israelis are understandably unnerved by this approach from President Trump". Recent Trump administration Middle East policies have increasingly sidestepped Israeli preferences.
Regional Security Implications
The June 2025 escalation between Israel and Iran has fundamentally altered regional security calculations. Israel's strikes against Iran's nuclear facilities created new strategic realities that pressure U.S. decision-making. The deployment of additional U.S. Air Force fighters to the region demonstrates the administration's commitment to regional deterrence.
However, the risk of escalation into broader regional conflict remains significant. The presence of U.S. forces in defensive roles creates potential for involvement in offensive operations should Iran target American personnel or assets.
Future Scenarios and Assessment
Most Likely: Enhanced Defensive Cooperation
Based on current evidence, the most probable outcome involves continued expansion of defensive cooperation without direct combat troop deployment. This scenario includes additional missile defense systems, enhanced intelligence sharing, and increased military aid while maintaining defensive operations. The THAAD deployment provides a template for direct U.S. military involvement in defensive roles that enhance Israeli capabilities without triggering War Powers Resolution requirements.
Moderate Probability: Limited Combat Support
A second scenario involves limited U.S. combat support in specific circumstances, particularly if Iran directly attacks U.S. forces. This could include air defense operations, protection of U.S. personnel, or limited strikes against Iranian assets threatening American interests. Such operations would likely be justified under inherent presidential authority to protect U.S. forces, though sustained combat would require congressional authorization.
Lowest Probability: Full Military Partnership
Direct U.S. participation in Israeli offensive operations represents the least likely scenario given current political and legal constraints. Such involvement would require either Congressional authorization or presidential determination of imminent threat to U.S. national security. The introduction of bipartisan war powers resolutions and divided public opinion create significant political obstacles.
Constitutional and Legal Analysis
Executive Authority Limitations
Current U.S. military involvement operates within established executive authority for defensive operations and emergency aid provision. However, sustained offensive operations would trigger constitutional requirements for congressional authorization. The War Powers Resolution's 60-day limit has not been triggered for current operations, as they are characterized as defensive.
The distinction between defensive and offensive operations becomes increasingly tenuous as U.S. forces enable Israeli military operations through intelligence and operational support. Critics argue that certain aspects of cooperation may raise questions about compliance with international humanitarian law.
Economic and Strategic Considerations
Defense Industrial Integration
U.S.-Israel military cooperation extends beyond aid transfers to encompass joint development and production programs. Israel's participation in the F-35 Lightning II development program creates deep industrial integration. This integration generates economic benefits while creating institutional momentum for continued cooperation.
The Heritage Foundation has proposed transitioning U.S.-Israel relations from aid dependence to strategic partnership by 2047. However, such proposals remain controversial and face significant opposition from pro-Israel constituencies.
Key Findings and Conclusions
Current Military Reality
The United States has already deployed military personnel to Israel in limited defensive roles, fundamentally altering U.S.-Israel cooperation. The deployment of 100 troops to operate the THAAD system represents direct American military presence on Israeli soil for the first time during the current conflict. This deployment, combined with extensive intelligence sharing and unprecedented military aid levels, demonstrates active military cooperation beyond traditional arms sales.
Legal and Political Constraints
Significant constraints exist on expanded U.S. military involvement. Constitutional requirements for congressional authorization, the War Powers Resolution framework, and bipartisan legislative efforts create substantial hurdles for combat troop deployment. Public opinion polling consistently shows American reluctance to deploy troops to the Middle East.
Most Probable Trajectory
Based on comprehensive analysis of current trends, legal frameworks, and political dynamics, the most probable scenario involves continued expansion of defensive military cooperation while avoiding direct combat engagement. This approach allows the U.S. to demonstrate commitment to Israeli security while maintaining constitutional governance and respecting public opinion constraints.
The fundamental question is not whether the U.S. will support Israel militarily – it already does extensively – but rather the extent to which defensive cooperation will expand into offensive participation. Current evidence suggests continued robust support through aid, intelligence, and defensive systems while avoiding direct combat roles that would constitute "joining Israel militarily" in the fullest sense.
Critical Factors for Future Escalation
Several factors could alter this trajectory toward expanded military involvement: direct Iranian attacks on U.S. forces would likely trigger more robust American military response; congressional authorization would remove current legal constraints, though this appears unlikely given current political dynamics; catastrophic regional escalation could create pressure for expanded involvement despite domestic constraints; and evidence of imminent Iranian nuclear weapons acquisition could generate support for military action.
This analysis demonstrates that U.S.-Israel military cooperation has already reached unprecedented levels through current troop deployments, intelligence sharing, and financial support. However, expansion into full military partnership faces significant constitutional, political, and public opinion constraints that currently limit the scope of American involvement in offensive operations.
The Kremlin is utilising the recent United States and Israeli military strikes on Iran to validate its ongoing war in Ukraine. Russian officials are pointing to the escalation in the Middle East as evidence that Western nations do not adhere to international rules.
Saudi Arabia’s state oil giant Saudi Aramco closed its Ras Tanura refinery on Monday following an Iranian drone strike, an industry source told Reuters as Tehran retaliated across the Gulf after a U.S.-Israeli attack on Iranian targets over the weekend.
The Middle East crisis intensifies after the deadly attack on the compound of the Supreme Leader of Iran Ali Khamenei on Saturday that killed him, other family members and senior figures. Iran has launched retaliatory strikes on U.S. targets in the region.
U.S. President Donald Trump said the U.S. military has enough stockpiled weapons to fight wars "forever"; in a social media post late on Monday. The remarks came hours before conflict in Iran and the Middle East entered its fourth day.
Türkiye raised its security level for Turkish-flagged vessels in the Strait of Hormuz to Level 3 on Sunday (2 March). The development follows Iranian restrictions on shipping after U.S. and Israeli strikes and confirmation of Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei’s death.
Strikes across the Middle East are intensifying, fuelling travel disruption, driving up global energy prices and forcing diplomatic missions to shut their doors as tensions continue to rise.
U.S. President Donald Trump has said the United States has a “virtually unlimited supply” of munitions and is capable of sustaining military action indefinitely, as the conflict with Iran entered its fourth day.
The United Nations has called for an investigation into a deadly attack on a girls’ primary school in Iran, which Iranian officials say has killed more than 100 children. The U.S. has said its forces “would not” deliberately target a school.
U.S. first lady, Melania Trump chaired a UN Security Council meeting on children and education in conflict on Monday (2 March), a move criticised by Iran as hypocritical following U.S. and Israeli strikes that triggered a UN warning about risks to children.
Start your day informed with AnewZ Morning Brief. Here are the top news stories for the 3rd of February, covering the latest developments you need to know.
You can download the AnewZ application from Play Store and the App Store.

What is your opinion on this topic?
Leave the first comment