Scientists have identified a long-lost group of hunter-gatherers who vanished from Colombia’s highlands 2,000 years ago, reshaping our understanding of ancient human migrations in South America.
A groundbreaking DNA analysis has revealed traces of a previously unknown indigenous population that lived in what is now Colombia—and vanished thousands of years ago without leaving a genetic legacy. The findings, published in Science Advances, suggest a complete population turnover in the Colombian Andes, where today’s capital, Bogotá, now stands.
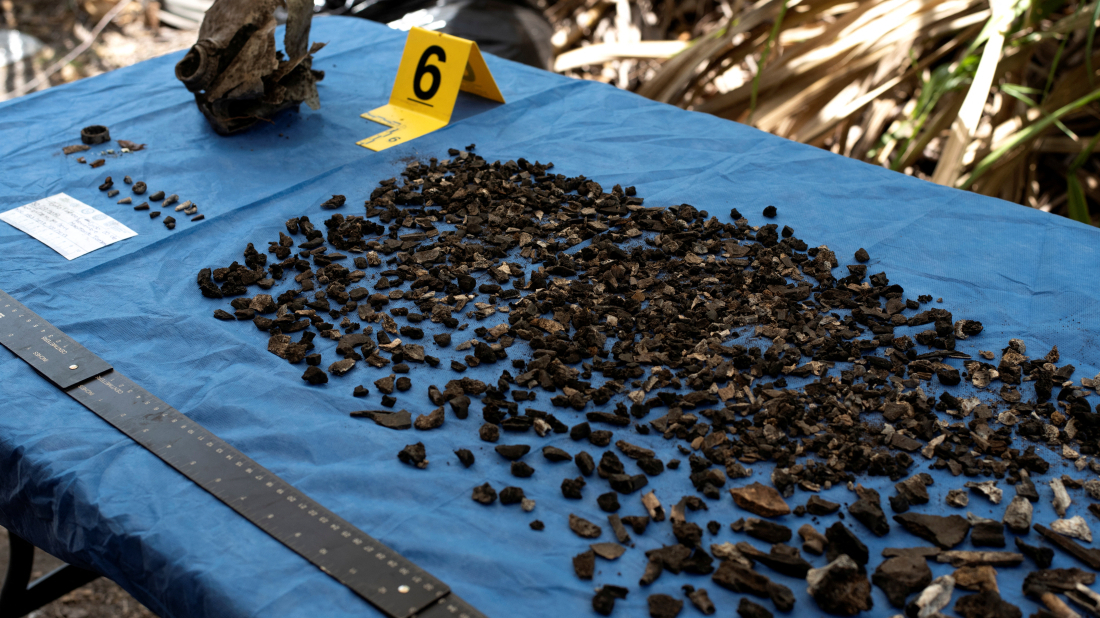
Researchers analyzed ancient DNA from 21 human skeletons unearthed at five archaeological sites on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, a high plateau in central Colombia. These included samples from different time periods, ranging from early hunter-gatherers who lived 6,000 years ago to more recent indigenous groups from just over 500 years ago.
The study found that the earliest group—hunter-gatherers who inhabited the Checua site 6,000 years ago—had unique genetic signatures that disappeared entirely around 4,000 years ago. “We have not been able to find any descendants of these early hunter-gatherers from the Colombian Highlands,” researchers noted. “That means there has been a complete population exchange around Bogotá.”
Later populations, including those from the Herrera and Muisca cultures, show genetic ties to groups that likely migrated from Central America, bringing with them new technologies such as ceramics. This suggests a major cultural and demographic shift took place between 6,000 and 2,000 years ago.
The Herrera period, beginning around 2,800 years ago, saw the rise of pottery and more complex settlement patterns. However, how these innovations reached the highlands had remained unclear until now. The genetic evidence strongly supports the theory that migrating populations introduced these cultural changes—replacing the earlier indigenous group entirely.
This study not only uncovers a lost chapter of human history in South America but also challenges long-held assumptions about cultural continuity among indigenous communities in the Andes.

















What is your opinion on this topic?
Leave the first comment